How much do we know about the dangers of fluorine? Low fluorine fluorine free fillers to lead the industry new fashion
Fluorine: An in-depth analysis of definitions, applications, and hazards
In the course of human exploration of materials, thermal and mechanical properties have been the core of development. However, with the progress of materials science, conventional materials have been able to easily meet the performance requirements of products, but environmental protection and health issues have become increasingly prominent. Among them, halogen-containing materials (such as PVC, halogen-containing flame retardants, etc.) have attracted much attention due to their potential harm to the environment and human body. Today, we'll focus on fluorine, exploring its definition, applications, and potential hazards.
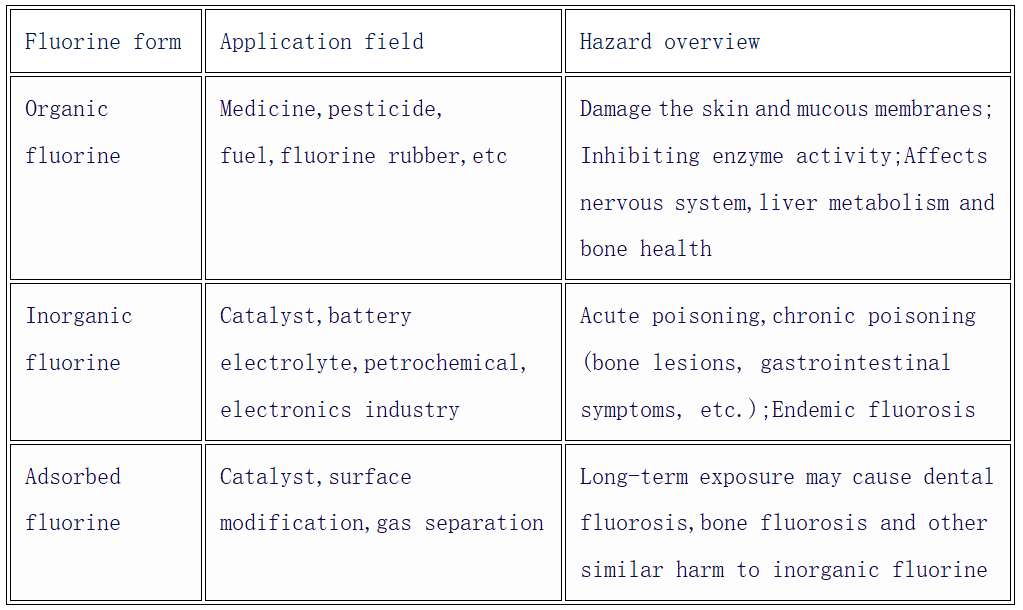
Morphology and classification of fluorine
Organic fluorine: organic compounds containing fluorine atoms, including organometallic compounds, which have the characteristics of low toxicity and high stability, and are widely used in medicine, pesticides, fuels and fluorine rubber and other fields.
Inorganic fluorine: Compounds, such as calcium fluoride and sodium fluoride, which are directly connected with other nonmetallic or metallic elements, and play an important role in the catalyst and battery electrolyte industries.
Adsorbed fluorine: Fluoride attached to a solid surface by physical or chemical adsorption. It may be inorganic or organic, depending on the adsorption source and conditions.
Application range and potential harm of fluorine
Generation and control of fluorine in non-mineral materials
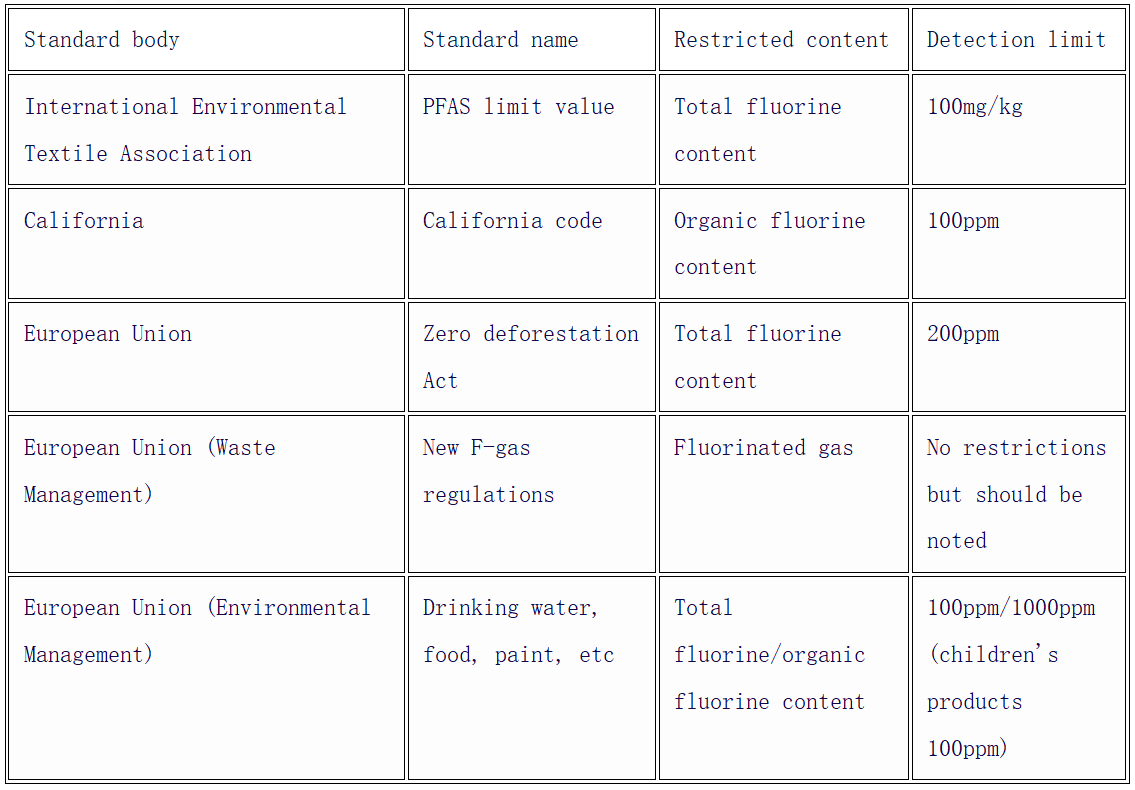
The fluorine in nonmetallic minerals may be derived from the residual fluoride in the mother rock of the original ore, or the adsorption of fluoride in the environment during the formation and weathering. At present, the control of fluorine in Europe and the United States is increasingly strict, and although the domestic standard regulations on relevant products have not yet been introduced, the environmental protection trend has been irreversible.
Overview of industry-related standards
Solution: Low to no fluorine inorganic fillers
Faced with the problem of high fluorine content in products, our company actively responds to the needs of environmental protection and health, and has developed a number of low fluorine to no fluorine inorganic fillers. These fillers can not only effectively reduce the fluorine content of the product, but also ensure the performance and quality of the product. If you need further understanding or cooperation, please continue to follow our public account or contact us directly.
Conclusion:
In today's increasing awareness of environmental protection and health, reducing the fluorine content in products has become a pain point that needs to be solved in many industries. We are committed to providing low fluorine to no fluorine inorganic filler solutions to help the industry towards a greener and healthier future. Let us work together to contribute to the health of the earth and human beings!




