Effect of talc on shrinkage of polypropylene
Polypropylene resin (PP) is widely used in automotive interior and exterior trim because of its low cost, excellent comprehensive mechanical properties, low temperature impact resistance and aging resistance. However, due to the shrinkage rate of polypropylene resin is generally 1.5%~2.0%, the shrinkage rate is larger, which brings a certain challenge to the dimensional stability of the molding products. The results show that the thermal deformation temperature of polypropylene can be increased by using Talc as filler, the shrinkage rate of polypropylene can be reduced, and the dimensional stability of polypropylene products can be improved. The commonly used process method in industry is to add a certain amount of talc to polypropylene, so as to obtain relatively low shrinkage polypropylene material.
Ⅰ.the effect of raw material components on the shrinkage rate of polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP), high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and EPDM are the matrix components of automotive interior and exterior trim composite materials. With polypropylene as the main material, high-density polyethylene and EPDM as additives, the mass ratio of the three is different, and the shrinkage rate of the material is also different, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Effects of HDPE, EPDM and Talc on PP shrinkage
PP dosage% | HDPE/EPDM dosage% | Talc dosage% | shrinkage% |
100 | 0 | 0 | 1.786 |
90 | 10 | 0 | 1.968 |
80 | 20 | 0 | 2.129 |
70 | 10 | 20 | 1.159 |
60 | 20 | 20 | 1.215 |
Note: The mass ratio of HDPE to EPDM is 1:1, and the Talc is 1250 mesh.
As can be seen from Table 1, the shrinkage rate of pure PP is 1.786%, while the shrinkage rate of HDPE and EPDM materials added is 1.968% and 2.129% respectively. In other words, the more HDPE and EPDM are used, the greater the shrinkage rate of materials will be. However, once Talc powder is added to the material, the shrinkage rate of the material is greatly reduced to about two-thirds of the value of pure PP. Therefore, HDPE and EPDM can improve the shrinkage rate of materials. The larger the dosage, the higher the shrinkage rate of materials. Talc powder, on the other hand, can greatly reduce the shrinkage rate of materials. Of course, when Talc powder is added, the shrinkage rate of the material is still affected by the amount of HDPE and EPDM. The larger the amount of HDPE and EPDM, the higher the shrinkage rate of the material, but the trend of improvement becomes slower.
Ⅱ.Influence of Talc dosage on polypropylene shrinkage
It is found in the experiment that the shrinkage rate of materials varies with the amount of Talc powder. Figure 1 shows the influence of the amount of Talc powder on the shrinkage rate of materials. As can be seen from Figure 1, with the increase of Talc powder dosage, the shrinkage rate of materials gradually decreases.
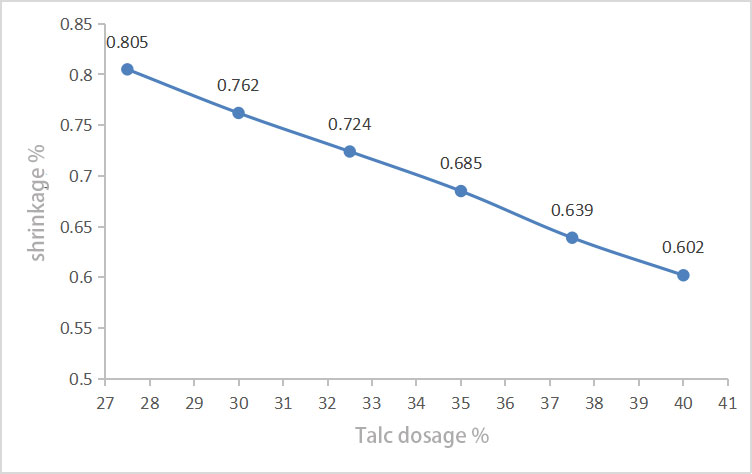
Figure 1. Effect of Talc powder dosage on polypropylene shrinkage
Talc powder is a mineral product with a thin sheet structure. As a rigid particle, its shrinkage rate is much lower than PP. Therefore, the addition of Talc powder plays a skeleton role for the composite material, making the polymer chains such as PP, HDPE and EPDM get good support in the forming process, reducing the "cantilever" and "hanging" phenomenon of the polymer chains, so as to improve the rigidity of the composite material on the whole and reduce the shrinkage rate of the composite material. The higher the amount of Talc powder , the more obvious the support effect of polymer chain, the lower shrinkage rate of composite material.
Ⅲ.the effect of Talc powder size polypropylene shrinkage rate
Table 2 shows the influence of Talc powder particle size on polypropylene. As can be seen from Table 2, when the dosage of Talc powder is 27.5% but the particle size is different, the shrinkage rates of both are 0.811% and 0.805%, respectively. That is, the smaller the particle size, the lower the shrinkage rate of the material with the same amount of Talc powder. This is because the flake structure of Talc powder will directly affect the density of composite materials. The flake size of T-1 is relatively large, and it is easy to appear "holes" when filling resin, which will lead to relatively large shrinkage of the material after injection molding.
At the same time, when Talc powder is filled into the resin, it acts as both a filler and a nucleating agent. Filler reduces the shrinkage rate of the material. Nucleating agent will prevent the formation of large spherules in the material, which will affect the crystallization of PP, and then reduce the shrinkage rate of the material. Because the particle size of T-2 (3000 mesh) is smaller than that of T-1 (1250 mesh), there are more particles of the same mass and more particles that can act as nucleating agents, the effect of hindering the formation of large spherules of the material is relatively better, resulting in a relatively low shrinkage rate of the overall material.
When T-1 and T-2 were added to the resin at the same time, it was found that the shrinkage rate of the material gradually decreased with the reduction of the amount of T-1 under the condition of a constant total Talc powder, but when the mass ratio of the two was 1:2, the shrinkage rate of the material reached the minimum value of 0.556%. Subsequently, with the increase of the amount of T-2, the shrinkage rate of the material actually increased. This is because the specific surface area of coarse particles is different from that of fine particles. The specific surface area of coarse particles is smaller than that of fine particles, and the shrinkage rate of materials will be affected by the number of contact surfaces between PP and Talc. The larger the contact interface between PP and Talc powder, the lower the shrinkage rate of materials.
However, when a single coarse particle or fine particle Talc powder is added, a large gap will be accumulated between particles, forming the so-called void effect, resulting in a decrease in the density of the material, and a large shrinkage rate of the overall material during molding; When the two kinds of coarse and fine particles are added to PP at the same time, the gaps between the particles are filled by fine particles, forming the so-called secondary filling effect. As a result, the compactness of the material increases and the overall shrinkage rate of the material is low.
Table 2 Influence of Talc powder particle size on polypropylene
PP dosage% | HDPE/EPDM dosage% | T-1 dosage% | T-2 dosage% | shrinkage% |
62.5 | 10 | 27.5 | 0 | 0.811 |
62.5 | 10 | 0 | 27.5 | 0.805 |
62.5 | 10 | 20 | 7.5 | 0.809 |
62.5 | 10 | 13.75 | 13.75 | 0.807 |
62.5 | 10 | 12 | 15.5 | 0.743 |
62.5 | 10 | 10 | 17.5 | 0.622 |
62.5 | 10 | 9.2 | 18.3 | 0.556 |
62.5 | 10 | 8 | 19.5 | 0.686 |
62.5 | 10 | 5 | 22.5 | 0.775 |
Note: The mass ratio of HDPE to EPDM is 1:1, T-1 is 1250 mesh Talc powder, T-2 is 3000 mesh Talc powder.
Conclusion: The addition of Talc can reduce the forming shrinkage rate of polypropylene materials. With the increase of Talc dosage, the forming shrinkage rate of polypropylene materials decreases gradually. The particle size of Talc also has a great influence on the shrinkage rate of materials. Under the same conditions, the finer Talc is, the lower the shrinkage rate of materials is. If two kinds of Talc with different thickness are added, the shrinkage rate of the material is the lowest when the mass ratio of them is 1:2 under the condition of a certain total mass.
Source: LIU Chaofu, Li Jing. Effect of Talc on shrinkage of polypropylene/Talc composite [J]. Plastics Science and Technology, 2014 (08) : 80-82




